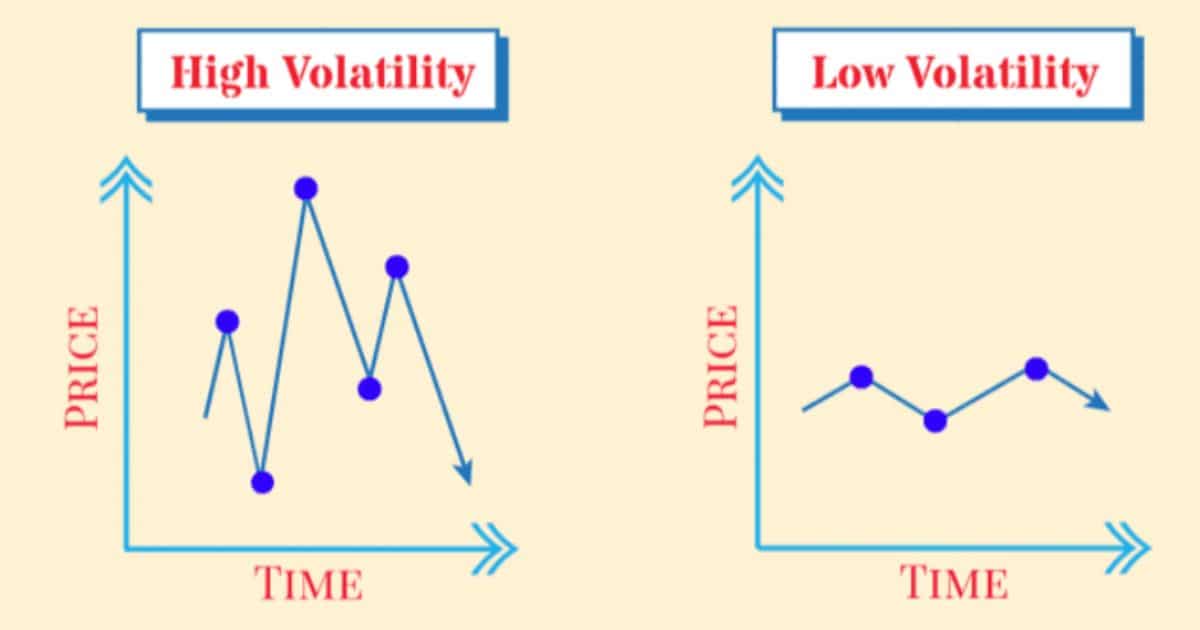
While some may argue that the level of volatility in a market is merely a reflection of short-term fluctuations and unpredictability, a deeper analysis reveals its crucial role in assessing and managing risk. Volatility serves as a measure of market uncertainty, allowing investors and analysts to gauge market sentiment and stability.
By understanding the implications of volatility, individuals can make informed investment decisions and navigate the dynamic landscape of financial markets. In this article, we delve into the significance of volatility and its impact on risk assessment.
Key Takeaways
- Volatility significantly influences the accuracy of risk assessment.
- Volatility is used as a measure of market uncertainty.
- High volatility can indicate increased fear and uncertainty among investors.
- Volatility helps identify undervalued assets and opportunities for profit.
The Impact of Volatility on Risk Assessment
The presence of volatility in a market significantly influences the accuracy of risk assessment. Volatility refers to the degree of variation in the price of a financial instrument or security over time. It is commonly measured by calculating the standard deviation of returns.
High levels of volatility indicate larger price swings, making it difficult to predict future price movements and assess potential risks accurately. In a volatile market, traditional risk assessment models may not be effective in capturing the true level of risk. This is because volatility introduces uncertainty and can lead to unexpected market developments.
Risk assessment models need to incorporate volatility measures to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the potential risks involved. By considering volatility, investors can better evaluate the likelihood and magnitude of potential losses, enabling them to make more informed decisions.
Volatility as a Measure of Market Uncertainty
Measuring market uncertainty can be achieved through assessing the level of volatility in a market. Volatility, in the context of financial markets, refers to the degree of variation or fluctuation in the prices of assets or securities. It is often used as a measure of market uncertainty because higher levels of volatility indicate greater price fluctuations and potential risks.
When markets are volatile, it suggests that there is a higher level of uncertainty and unpredictability in the market. This can be attributed to various factors such as economic conditions, political events, or investor sentiment. By analyzing volatility, investors and market participants can gain insights into the level of uncertainty and make informed decisions regarding their investments and risk management strategies.
Volatility serves as an important tool for understanding market dynamics and assessing the level of uncertainty that investors may face.
Analyzing Market Sentiment Through Volatility
Assessing market sentiment can be achieved through analyzing the impact of volatility on investor behavior and market trends. When analyzing market sentiment through volatility, the following factors should be considered:
- Fear and Uncertainty: High volatility can indicate increased fear and uncertainty among investors, leading to market sell-offs and a decline in stock prices.
- Risk Appetite: Low volatility suggests that investors have a higher risk appetite and are more confident in the market, leading to increased buying activity.
- Investor Confidence: Volatility can reflect the level of investor confidence in the market. High volatility may indicate a lack of confidence, while low volatility suggests a more optimistic outlook.
- Market Trends: Volatility can provide insights into market trends. Rapid price fluctuations may indicate changing trends or the emergence of new investment opportunities.
- Market Reactions: Analyzing volatility can help identify how the market reacts to specific events or news. Understanding these reactions can provide valuable insights into investor sentiment.
Analyzing market sentiment through volatility allows investors to make informed decisions based on the prevailing market conditions. Transitioning into the next section, we will explore the relationship between volatility and the stability of the market.
Volatility and the Stability of the Market
Volatility in a market can both reflect and influence the stability of market conditions. When market volatility is high, it indicates that prices are fluctuating rapidly and unpredictably, which can create an environment of uncertainty and instability. On the other hand, when volatility is low, it suggests that prices are relatively stable, and market conditions are more predictable.
To better understand the relationship between volatility and market stability, let’s take a look at the following table:
| Market Volatility | Market Stability |
|---|---|
| High | Low |
| Low | High |
| Moderate | Moderate |
As shown in the table, high volatility corresponds to low market stability, while low volatility corresponds to high market stability. Moderate volatility indicates a balance between stability and unpredictability.
Understanding the relationship between volatility and market stability is crucial for investors as it helps them assess the level of risk associated with their investments. By analyzing market volatility, investors can make more informed decisions to maximize their returns while minimizing potential losses. In the next section, we will explore how to utilize volatility to make informed investment decisions.
Utilizing Volatility to Make Informed Investment Decisions
Investors can leverage market volatility to inform their investment decisions and enhance their potential for financial gain. By understanding and utilizing volatility, investors can identify opportunities for profit and mitigate risks. Here are five ways investors can use market volatility to make informed investment decisions:
- Identify undervalued assets: Volatility often leads to mispriced assets, providing opportunities for investors to buy low and sell high.
- Determine risk appetite: Volatility can indicate the level of risk in the market, allowing investors to adjust their portfolios accordingly.
- Timing investments: Volatility can signal potential turning points in the market, enabling investors to enter or exit positions at opportune times.
- Identify trends: Volatility patterns can reveal market trends, helping investors identify sectors or industries with growth potential.
- Utilize options and derivatives: Volatility can increase the value of options and derivatives, allowing investors to hedge against potential losses or speculate on price movements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Some Common Factors That Contribute to Market Volatility?
Common factors contributing to market volatility include economic indicators, geopolitical events, investor sentiment, interest rates, corporate earnings, and market liquidity. These factors can create uncertainty and drive fluctuations in prices, leading to higher levels of volatility in the market.
How Can Market Volatility Affect Different Types of Investments?
Market volatility can have varying effects on different types of investments. For example, high volatility can lead to increased risk and potential losses for stocks, while it may present opportunities for traders in the options market.
Are There Any Strategies to Mitigate the Impact of Market Volatility on Investment Portfolios?
Strategies to mitigate the impact of market volatility on investment portfolios can include diversification, hedging, and active management. These approaches aim to reduce risk exposure and protect against adverse market movements, ultimately preserving portfolio value.
Can Market Volatility Be Predicted or Forecasted?
Market volatility refers to the degree of fluctuation in prices within a market. It is a measure of the uncertainty and risk associated with investing in that specific market, and can impact investment decisions and portfolio performance.
Is There a Correlation Between Market Volatility and Economic Indicators or Events?
There is a growing interest in understanding the correlation between market volatility and economic indicators or events. Research indicates that certain economic indicators can influence market volatility, but the extent of this relationship is complex and subject to various factors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, What Is Market Volatility serves as a crucial measure of market uncertainty and risk assessment. By analyzing market sentiment through volatility, investors can make informed investment decisions. Volatility also reflects the stability of the market, providing valuable insights for market participants.
Understanding and utilizing volatility as a data-driven tool can greatly enhance investment strategies and improve financial outcomes. As the saying goes, “Volatility is the spice of the market, adding flavor and excitement to investment opportunities.”