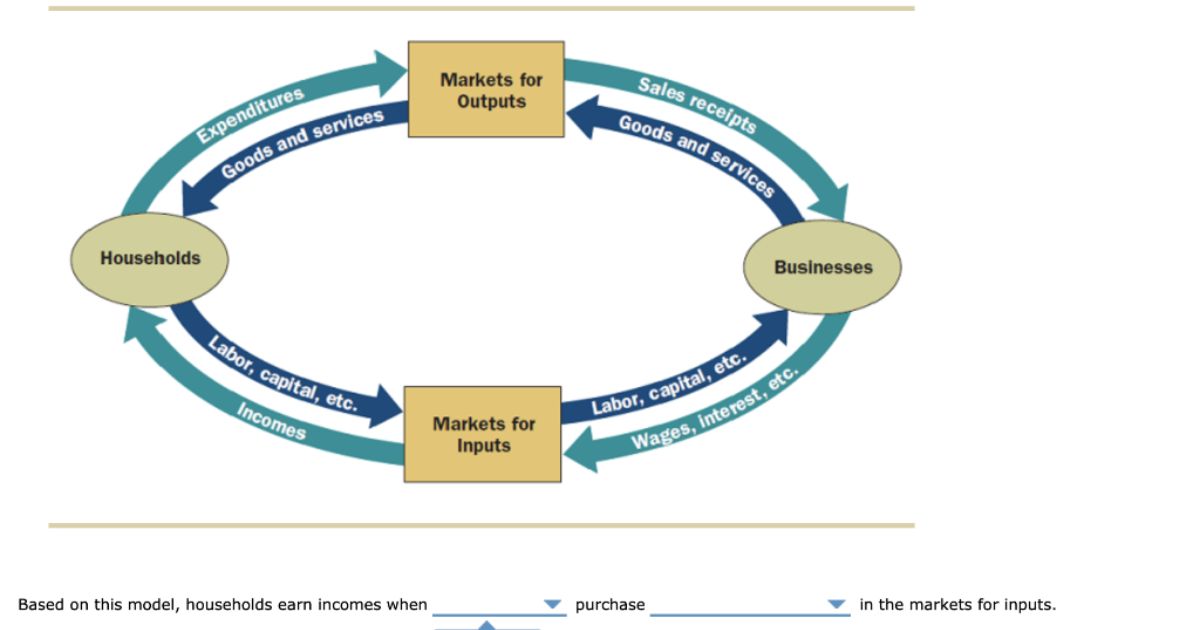
In the intricate web of economic interdependence, various markets play a pivotal role in driving the circular flow of goods and services. From the bustling Goods and Services Markets to the dynamic Labor and Financial Markets, each sector contributes to the intricate tapestry of economic activity.
This article delves into the fundamental markets represented in the simple circular flow diagram, offering a technical and evidence-based analysis of their significance. Join us as we navigate the vast landscape of economic markets and explore their role in fostering prosperity and growth.
Key Takeaways
- The Simple Circular Flow Diagram represents various markets, including the Goods Market, Services Market, Labor Market, Financial Market, and Resource Market.
- Factors such as supply and demand in the labor market, resource market, foreign exchange market, and real estate market have a significant impact on market dynamics and outcomes.
- Participants in the resource market include individuals, firms, resource owners, government, and financial institutions, each playing a crucial role in the allocation and utilization of resources.
- The government market has a substantial impact on the economy through assistance programs, regulations, provision of public goods, government spending and taxation, and interactions with other markets.
The Goods Market
The goods market plays a crucial role in the simple circular flow diagram as it represents the exchange of finished goods and services between households and firms. This market is an essential part of the economy, as it allows for the production, distribution, and consumption of goods.
In this market, households act as consumers, purchasing goods and services from firms. On the other hand, firms act as producers, supplying goods and services to households. The goods market is characterized by the buying and selling of tangible products, such as groceries, clothing, and electronics.
It is a dynamic market that constantly adjusts to changes in consumer demand and production capabilities. The presence of a well-functioning goods market is vital for economic growth and development, as it ensures the efficient allocation of resources and promotes overall prosperity.
The Services Market
One key market in the simple circular flow diagram is the services market, which represents the exchange of intangible services between households and firms. The services market plays a crucial role in the economy by providing a wide range of services such as healthcare, education, transportation, and professional services. In this market, households pay firms for the services they provide, while firms hire individuals to perform these services.
The services market is characterized by its intangible nature, as services cannot be stored or physically possessed. This market is essential for the smooth functioning of the economy as it meets the diverse needs and demands of households, contributing to economic growth and development. Overall, the services market is an integral part of the circular flow of income and expenditure, connecting households and firms in a mutually beneficial exchange of services.
The Labor Market
The labor market is an essential component of the simple circular flow diagram. It involves the exchange of labor services between workers and firms. The wage determination factors, such as skills, education, and experience, play a crucial role in determining the wages workers receive.
Supply and demand dynamics in the labor market also influence wage levels and the allocation of labor resources. The labor market reaches equilibrium when the quantity of labor supplied equals the quantity of labor demanded at a specific wage rate.
Wage Determination Factors
Several factors influence wage determination in the labor market. These factors are complex and interdependent, and understanding them is crucial for both employers and employees.
Here are five key factors that contribute to wage determination:
- Skill level: Wages are often determined by the level of skills and qualifications required for a particular job. Highly skilled workers tend to command higher wages due to their specialized knowledge and expertise.
- Demand and supply: The demand and supply of labor play a significant role in wage determination. When the demand for a specific skill is high and the supply is low, wages tend to increase as employers compete for qualified workers.
- Education and experience: Higher levels of education and relevant work experience can lead to higher wages. Employers often value individuals with advanced degrees or extensive experience in a particular field.
- Labor market conditions: The overall health of the labor market, including factors such as unemployment rates and economic growth, can influence wage levels. In times of economic prosperity, wages may rise due to increased demand for labor.
- Collective bargaining: In some cases, wages are determined through collective bargaining between employers and labor unions. These negotiations can result in higher wages and additional benefits for workers.
Understanding these wage determination factors is essential for both employers and employees to ensure fair compensation and a thriving labor market. By considering these factors, employers can attract and retain skilled workers, while employees can make informed decisions about their career paths and negotiate appropriate wages.
Supply and Demand
In order to understand the dynamics of the labor market, it is important to examine the relationship between supply and demand. The labor market operates like any other market, with employers demanding labor and workers supplying their skills and services. The interaction between the supply and demand for labor determines the equilibrium wage rate and employment level in the market.
The table below illustrates the relationship between supply and demand in the labor market:
| Factors affecting labor supply | Factors affecting labor demand |
|---|---|
| Population growth | Economic conditions |
| Education and training | Technological advancements |
| Immigration | Industry trends |
| Government policies | Consumer demand |
The labor market is influenced by various factors on both the supply and demand sides. An increase in population growth or immigration can lead to an increase in labor supply, while economic conditions and industry trends affect labor demand. Additionally, education and training, technological advancements, and government policies also play a significant role in shaping the labor market dynamics.
Understanding the relationship between supply and demand in the labor market is essential for policymakers, employers, and workers to make informed decisions regarding wages, employment opportunities, and labor market regulations.
Labor Market Equilibrium
To achieve labor market equilibrium, employers and workers must negotiate a fair wage rate that balances labor supply and demand. This equilibrium occurs when the quantity of labor supplied by individuals matches the quantity demanded by employers. Here are five key factors that influence labor market equilibrium:
- Skills and qualifications of workers
- Demographic changes in the labor force
- Technological advancements and automation
- Government policies and regulations
- Economic conditions and business cycles
Understanding these factors is crucial for both job seekers and employers to navigate the labor market effectively. By considering these influences, individuals can make informed decisions about their career paths, while businesses can strategize their hiring and workforce planning. Transitioning to the subsequent section about the financial market, it is important to explore how labor market equilibrium impacts economic stability and growth.
The Financial Market
Representing the flow of funds and capital, the financial market plays a vital role in facilitating investment, borrowing, and lending activities within an economy. It serves as a platform where individuals, businesses, and governments can access the necessary capital to fund their operations and projects. The financial market can be broadly categorized into two main components: the money market and the capital market.
| Money Market | Capital Market |
|---|---|
| Short-term debt | Long-term debt |
| Instruments | Instruments |
| Maturity | Maturity |
| Less risky | More risky |
In the money market, short-term debt instruments are traded, typically with a maturity of less than one year. This market provides liquidity and stability to the financial system by allowing participants to invest in low-risk instruments such as Treasury bills and commercial paper. On the other hand, the capital market deals with long-term debt and equity instruments, with a maturity exceeding one year.
This market enables businesses and governments to raise long-term funds through the issuance of bonds and stocks. However, the capital market carries higher risk compared to the money market due to the longer maturity and potential fluctuations in value. Overall, the financial market is crucial for efficient allocation of resources and capital formation in an economy.
The Resource Market
The resource market is a key component of the simple circular flow diagram, representing the market for different types of resources. These resources include land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. The interaction of supply and demand in the resource market determines resource prices, which in turn affects the allocation of resources in the economy.
Participants in the resource market include individuals, businesses, and the government, all of whom play a role in the buying and selling of resources.
Types of Resources
An important aspect of the Simple Circular Flow Diagram is understanding the various types of resources that are involved in the resource market. Resources can be categorized into different types, each playing a crucial role in the production process.
Here are five key types of resources:
- Land: This refers to all natural resources, such as forests, minerals, and water, which are used in the production of goods and services.
- Labor: This includes all human effort, skills, and knowledge utilized in the production process.
- Capital: Capital resources are man-made tools, equipment, and machinery used to produce goods and services.
- Entrepreneurship: This involves the organization and coordination of resources to create and manage a business venture.
- Technology: Technological resources include the knowledge, techniques, and processes used to improve production efficiency and innovation.
Understanding the different types of resources helps us comprehend how they flow in the resource market and contribute to the overall circular flow of the economy.
Supply and Demand
Both supply and demand play a crucial role in the resource market of the Simple Circular Flow Diagram. In this market, individuals and firms interact to determine the allocation of resources. Supply refers to the quantity of resources that producers are willing and able to provide, while demand represents the quantity of resources that consumers are willing and able to purchase.
The interaction between supply and demand in the resource market determines the equilibrium price and quantity of resources. When the demand for resources increases, it leads to a higher price and an increase in the quantity of resources supplied. Conversely, if the demand decreases, it results in a lower price and a decrease in the quantity of resources supplied. Understanding supply and demand in the resource market is essential for policymakers and individuals seeking to make informed decisions about resource allocation.
Resource Market Participants
As individuals and firms are key players in the resource market, they interact with each other to determine the allocation of resources in the Simple Circular Flow Diagram. The resource market participants include:
- Individuals: They offer their labor, skills, and time in exchange for wages or salaries.
- Firms: They demand resources such as labor, capital, and natural resources to produce goods and services.
- Resource owners: These are individuals or entities that own and supply resources such as land, capital, and entrepreneurship.
- Government: It plays a role in the resource market by providing regulations, subsidies, and incentives that affect the allocation of resources.
- Financial institutions: They facilitate the flow of funds between individuals, firms, and government, allowing for investment in resources and economic growth.
The Capital Market
The Capital Market in the simple circular flow diagram represents the interaction between borrowers and lenders for the exchange of financial capital. This market plays a crucial role in the economy by facilitating the flow of funds from those who have surplus capital to those who need it. In the capital market, borrowers, such as businesses and governments, seek funds to finance their projects or operations, while lenders, such as individuals and institutions, provide the necessary capital. This interaction is essential for economic growth and development.
To further understand the participants and functions of the capital market, let’s look at the following table:
| Participants | Functions |
|---|---|
| Borrowers | Seek funds to finance projects or operations |
| Lenders | Provide capital for investment or lending purposes |
The Foreign Exchange Market
Many participants and various currencies are involved in the foreign exchange market, as it serves as a global marketplace for the buying and selling of different national currencies. Here are some key points about the foreign exchange market:
- It is the largest financial market in the world, with daily trading volumes exceeding $6 trillion.
- The market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, allowing participants from around the world to trade at any time.
- The main participants in the market include commercial banks, central banks, multinational corporations, and individual investors.
- Currency exchange rates are determined by supply and demand dynamics in the market, influenced by factors such as economic indicators, interest rates, and geopolitical events.
- The foreign exchange market plays a crucial role in facilitating international trade and investment, as it enables the conversion of one currency into another, thereby providing liquidity and reducing currency risk.
The Real Estate Market
Several key players, including buyers, sellers, and investors, participate in the real estate market, making it a dynamic and essential sector of the economy. The real estate market refers to the buying, selling, and leasing of property, including residential, commercial, and industrial properties.
This market is influenced by various factors, such as supply and demand, interest rates, government policies, and economic conditions. Buyers in the real estate market can be individuals or businesses looking to acquire property for personal use, investment, or development purposes. Sellers, on the other hand, can be homeowners, developers, or investors looking to sell their properties for profit. Investors play a crucial role in the real estate market by providing capital and driving market activity.
Overall, the real estate market plays a significant role in the economy by providing housing, facilitating business activities, and generating employment opportunities.
The Government Market
Occasionally, government intervention in the economy creates a distinct market known as the government market. This market consists of transactions between the government and other economic agents, such as individuals, businesses, and foreign entities.
The government market plays a crucial role in the economy by providing public goods and services, regulating markets, and redistributing income. Here are some key features of the government market:
- Government purchases: The government buys goods and services from businesses, such as defense equipment, infrastructure projects, and healthcare services.
- Taxes: The government collects taxes from individuals and businesses to finance its activities and redistribute income.
- Transfers: The government provides financial assistance to individuals and businesses through programs like welfare, unemployment benefits, and subsidies.
- Regulations: The government enforces rules and regulations to ensure fair competition, consumer protection, and environmental sustainability.
- Public goods: The government provides non-excludable and non-rivalrous goods like national defense, public parks, and street lighting.
The government market operates alongside other markets in the economy, and its activities have a significant impact on economic outcomes and the overall welfare of society.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does the Simple Circular Flow Diagram Represent the Interaction Between the Goods Market and the Services Market?
The simple circular flow diagram represents the interaction between the goods market and the services market by illustrating the flow of goods and services from firms to households and the flow of money from households to firms.
What Role Does the Labor Market Play in the Simple Circular Flow Diagram?
The labor market plays a crucial role in the simple circular flow diagram as it represents the exchange of labor services between households and businesses. It is an essential component in the flow of income and production.
How Are Financial Markets Represented in the Simple Circular Flow Diagram?
Financial markets play a crucial role in the simple circular flow diagram as they represent the flow of money between households and firms. They facilitate the exchange of financial assets such as stocks, bonds, and currencies, enabling the allocation of funds and investment opportunities.
Is the Resource Market Included in the Simple Circular Flow Diagram? if So, How Does It Fit Into the Overall Model?
The resource market is indeed included in the simple circular flow diagram, representing the exchange of resources (such as labor and capital) between households and firms. It plays a crucial role in the overall model by facilitating the production and allocation of goods and services.
Does the Simple Circular Flow Diagram Account for Interactions With International Markets, Such as the Foreign Exchange Market?
The simple circular flow diagram does not explicitly account for interactions with international markets such as the foreign exchange market. It focuses on the domestic flow of goods, services, and income within an economy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the simple circular flow diagram represents various markets including the goods market, services market, labor market, financial market, resource market, capital market, foreign exchange market, real estate market, and government market. These markets interact and facilitate the flow of goods, services, labor, and resources in the economy.
The diagram offers a visual representation of the interconnectedness and complexity of these markets, highlighting the crucial role they play in the functioning of the economy. Through this illustration, we gain a deeper understanding of the dynamic nature of economic transactions and the interdependencies among different market sectors.